Brain cells that control anxiety and stress-related mental disorders identified
Advances in microscopic imaging have led to the exciting discovery of a small group of brain cells that control stress-induced responses.
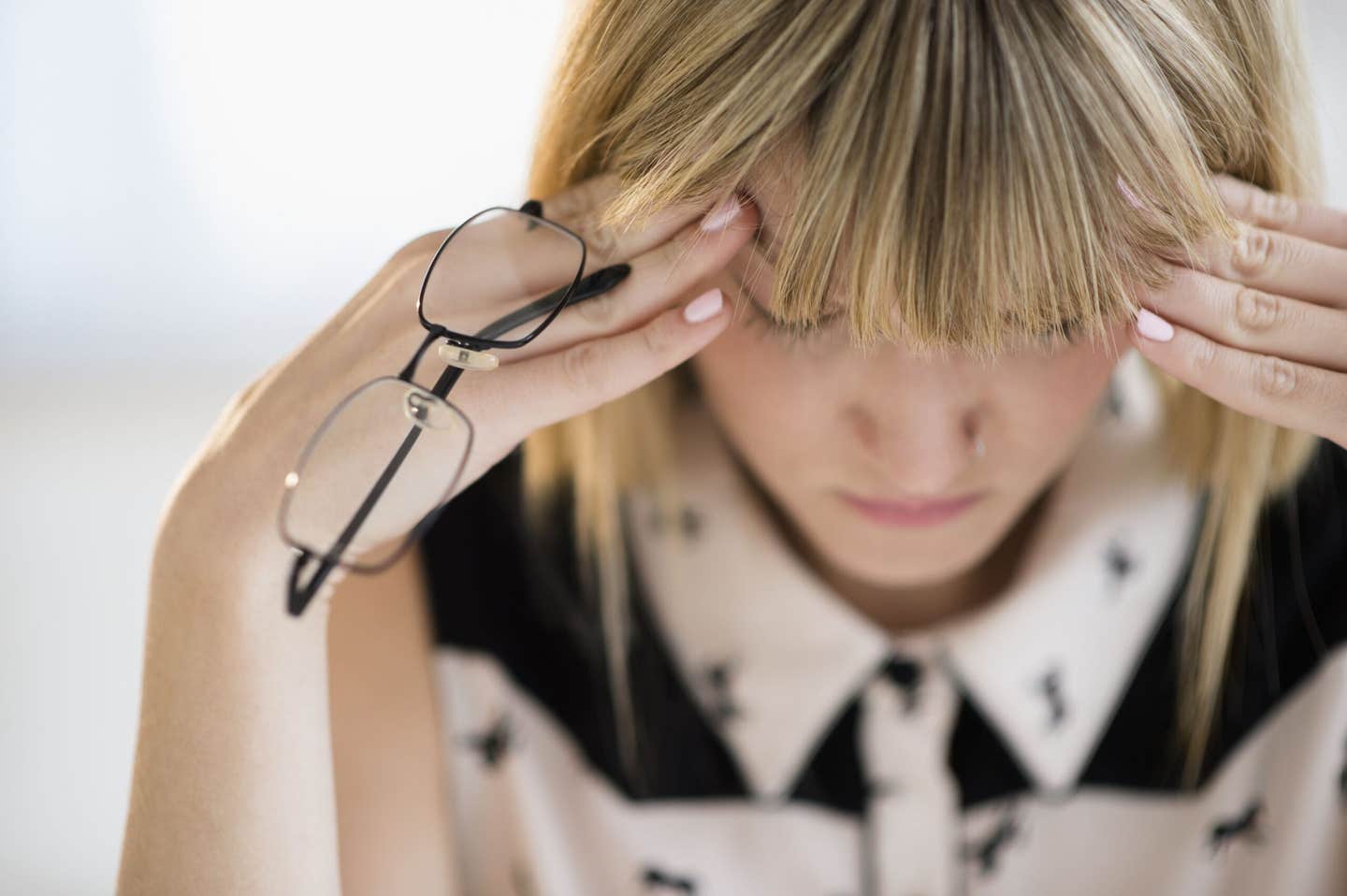

[Mar 21, 2022: Saori Obayashi, Osaka University]
Recent advances in microscopic imaging have led to the exciting discovery of a small group of brain cells that control stress-induced responses. (CREDIT: Creative Commons)
Osaka, Japan – It is well known that long-term exposure to stress can lead to serious psychiatric problems. However, the precise mechanisms underpinning the stress response have remained largely elusive. Recent advances in microscopic imaging by researchers from Japan have led to the exciting discovery of a small group of brain cells that control stress-induced responses. These cells could be the key to understanding the origin of stress-related mental disorders.
In a study published this month in Science Advances, researchers from Osaka University discovered a small group of brain cells in the claustrum of mice that controls stress-induced anxiety behaviors. When these cells were activated using chemogenetic technology, mice exhibited anxiety-related behaviors, whereas deactivation of the cells made mice more resilient against chronic stress.
Until recently, the identification of such small populations of cells using an unbiased and hypothesis-free approach has been challenging because of technical limitations. Now, the recent development of block-face serial microscopy tomography (known as FAST) by researchers at Osaka University has made this possible. This technique allowed the researchers to examine changes in cellular activity at the resolution of a single cell.
It is widely understood that the processing of stress relies on the communication between cortical and subcortical regions of the brain; however, the exact mechanism underlying this communication is uncertain, which is what the researchers aimed to uncover using this technique.
Related News
The researchers used well-established psychological animal models of restraint and social defeat stress to map patterns of cellular activity in mice that were exposed to stress.
Activation of the claustrum, identified as a reliable marker of the stressed brain, controls stress-induced anxiety-like and depression-like behaviors. (CREDIT: Atsushi Kasai)
Using the FAST technique, the team collected whole-brain images of control mice and mice exposed to these stressful conditions. Of the 22 brain regions studied, the claustrum was identified as a key region that differentiated stressed brains from non-stressed brains: “A combined approach using brain activation mapping and machine learning showed that the claustrum activation serves as a reliable marker of exposure to acute stressors,” say lead authors Misaki Niu and Atsushi Kasai.
Crucially, by manipulating the activity of these cells using chemogenetic technology, they concluded that the claustrum is crucial for the control of stress-induced anxiety-related behaviors. When the activity of these cells was amplified, mice exhibited anxious behaviors; these could then be reversed by suppressing claustrum cell activity.
“Inactivation of stress-responsive claustrum neurons can serve as at least a partially preventative measure for the emergence of depression-like behavior, and moreover, for stress susceptibility to increase resilience to emotional stress,” explains senior author Hitoshi Hashimoto.
This exciting discovery opens new opportunities for claustrum activity as a new treatment target for anxiety-related conditions and gaining a better understanding of the cause of stress-related disorders.
The article, “Claustrum mediates bidirectional and reversible control of stress-induced anxiety responses,” was published in Science Advances.
For more science and technology stories check out our New Discoveries section at The Brighter Side of News.
Note: Materials provided above by Osaka University. Content may be edited for style and length.
Like these kind of feel good stories? Get the Brighter Side of News' newsletter.
Tags: #New_Discoveries, #Science, #Research, #Brain, #Stress, #Anxiety, #Mental_Health, #Medical_News, #The_Brighter_Side_of_News