Researchers improve short term memory problems through laser therapy
Researchers demonstrated that the therapy, which is non-invasive, could improve short term, or working memory in people by up to 25%.
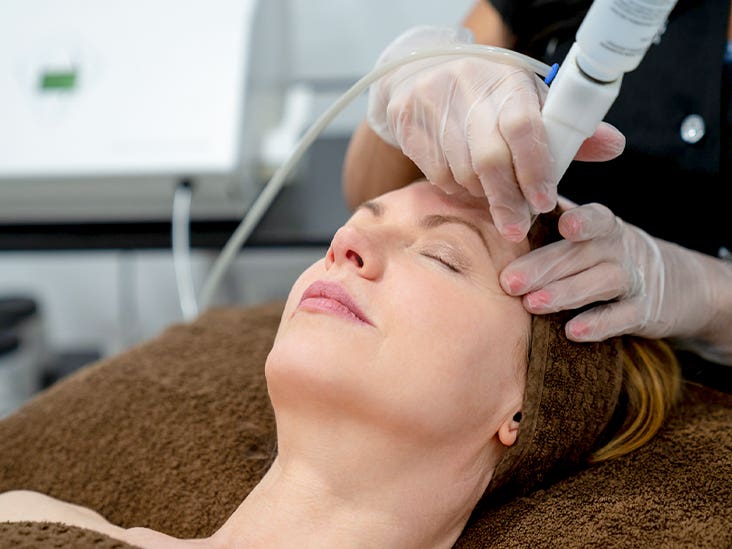
[Dec 5, 2022: Beck Lockwood, University of Birmingham]
Researchers demonstrated that the therapy, which is non-invasive, could improve short term, or working memory in people by up to 25%. (CREDIT: Creative Commons)
Laser light therapy has been shown to be effective in improving short term memory in a study published in Science Advances.
Scientists at the University of Birmingham in the UK and Beijing Normal University in China, demonstrated that the therapy, which is non-invasive, could improve short term, or working memory in people by up to 25 per cent.
The treatment, called transcranial photobiomodulation (tPBM), is applied to an area of the brain known as the right prefrontal cortex. This area is widely recognised as important for working memory. In their experiment, the team showed how working memory improved among research participants after several minutes of treatment.
They were also able to track the changes in brain activity using electroencephalogram (EEG) monitoring during treatment and testing.
Related Stories
Previous studies have shown that laser light treatment will improve working memory in mice, and human studies have shown tPBM treatment can improve accuracy, speed up reaction time and improve high-order functions such as attention and emotion.
This is the first study, however, to confirm a link between tPBM and working memory in humans.
Dongwei Li, a visiting PhD student in the University of Birmingham’s Centre for Human Brain Health, is co-author on the paper. He said: “People with conditions like ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder) or other attention-related conditions could benefit from this type of treatment, which is safe, simple and non-invasive, with no side-effects.”
Protocol, task, and behavioral results in experiments 1 and 2. tPBM protocol. Active tPBM was delivered by a laser with 1064 nm to the right PFC for a total of 12 min. Experimental protocol. Each participant received two tPBM sessions (active and sham, randomized, and double-blinded design) separated by 1 week. (CREDIT: Science Advances)
In the study researchers at Beijing Normal University carried out experiments with 90 male and female participants aged between 18 and 25. Participants were treated with laser light to the right prefrontal cortex at wavelengths of 1064 nm, while others were treated at a shorter wavelength, or treatment was delivered to the left prefrontal cortex. Each participant was also treated with a sham, or inactive, tPBM to rule out the placebo effect.
After tPBM treatment over 12 minutes, the participants were asked to remember the orientations or colour of a set of items displayed on a screen. The participants treated with laser light to the right prefrontal cortex at 1064 nm showed clear improvements in memory over those who had received the other treatments. While participants receiving other treatment variations were about to remember between 3 and 4 of the test objects, those with the targeted treatment were able to recall between 4 and 5 objects.
Grand average of ERPs and its link with behavior. (A) The orientation WM task in experiment 1 and (B) the color WM task in experiment 2. Shading indicates the CDA set-size effect. The enlarged black dots on EEG topographies show PO7/PO8 electrodes. Bar plots represent the average CDA set-size effect. Error bars represent SEM. Significant set-size effects are located in the IPS. Three-dimensional (3D) brain map (t-map; posterior view) of significant tPBM effect on CDA. (CREDIT: Science Advances)
Data, including from electroencephalogram (EEG) monitoring during the experiment was analysed at the University of Birmingham and showed changes in brain activity that also predicted the improvements in memory performance.
The researchers do not yet know precisely why the treatment results in positive effects on working memory, nor how long the effects will last. Further research is planned to investigate these aspects.
Grand average of ERPs and its link with behavior. (C) tPBM-effect. K values and CDA set-size effect for the two tasks (orientation WM task and color WM task) and two sessions (active tPBM and sham tPBM). (D) Scatterplots of participants’ behavioral benefits (active minus sham) against the changes in the CDA set-size effect (active minus sham) for the orientation WM task (gray) and the color WM task (black). *P
Professor Ole Jensen, also at the Centre for Human Brain Health, said: “We need further research to understand exactly why the tPBM is having this positive effect, but it’s possible that the light is stimulating the astrocytes – the powerplants – in the nerve cells within the prefrontal cortex, and this has a positive effect on the cells’ efficiency.
We will also be investigating how long the effects might last. Clearly if these experiments are to lead to a clinical intervention, we will need to see long-lasting benefits."
Note: Materials provided by University of Birmingham. Content may be edited for style and length.
Like these kind of feel good stories? Get the Brighter Side of News' newsletter.



